Rank
37 of 50
Economic Capital Ratio
23.21%
Trend (+/- rank to previous year)
-6.0
Summary
The relative strengths and weaknesses of Upstart Holdings Inc are analyzed with respect to the market average, including all of its competitors. We analyzed all variables having an effect on the Economic Capital Ratio.
The greatest strength of Upstart Holdings Inc compared to the market average is the variable Investments, increasing the Economic Capital Ratio by 97% points.The greatest weakness of Upstart Holdings Inc is the variable Debt, reducing the Economic Capital Ratio by 103% points.
The company’s Economic Capital Ratio, given in the ranking table, is 23%, being 24% points below the market average of 47%.
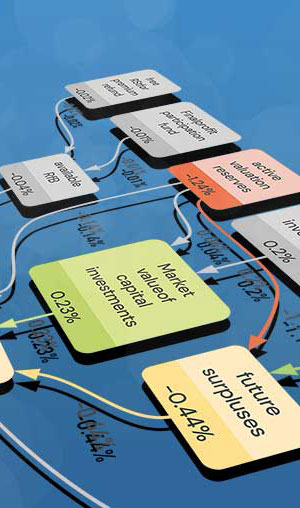
AI Causal Graph
The AI Causal Graph delineates the true determinants of financial strength. At the top of the graph, data from public annual reports is inputted. These variables are synthesized to ultimately produce the Economic Capital Ratio. Green nodes signify the company's strengths relative to the market average, enhancing financial robustness, whereas red nodes indicate weaknesses.
Causal Effects
The Causal Effects in each node indicate the individual impact of that variable on the final node, the Economic Capital Ratio. They reveal the extent to which the Economic Capital Ratio increases or decreases relative to the industry average. Cumulatively, these effects contribute to the overall Economic Capital Ratio.
| Name | Effect in % Points |
|---|---|
| Cash and Current Assets | -34.6 |
| Assets | -27.0 |
| Stockholders Equity | -32.2 |
| Economic Capital Ratio | -24.2 |
| Intangible Assets | -14.2 |
| Other Assets | -42.4 |
| Investments | 97.2 |
| Labor Expense | 26.3 |
| Expenses | -29.8 |
| Net Income | -31.5 |
| Other Expenses | 25.6 |
| Selling and General Administrative Expense | -31.5 |
| Operating Expenses | -59.1 |
| Debt | -103 |
| Loans Payable | 8.07 |
| Operating and Employee Liabilities | 23.4 |
| Other Liabilities | 42.0 |
| Other Revenues | 38.4 |
| Comprehensive Net Income | -31.3 |
| Revenue from Contract with Customer | -30.8 |
| Other Net Income | -5.34 |
Input Variables
The Input Variables consist of the absolute values from the public annual report data entered into the valuation model.
| Input Variables | in 1000 USD |
|---|---|
| Cash and Current Assets | 0 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 0 |
| Debt | 1,040,424 |
| Deposits and Payables to Customers | 71,438 |
| Depreciation Interest and Fees Expenses | 0 |
| Intangible Assets | 67,062 |
| Investment Income | 0 |
| Investments | 1,211,107 |
| Labor Expense | 0 |
| Loans Income | 0 |
| Loans Payable | 0 |
| Operating Expenses | 770,087 |
| Operating and Employee Liabilities | 62,324 |
| Other Assets | 738,931 |
| Other Compr. Net Income | 0 |
| Other Expenses | -339,424 |
| Other Liabilities | 207,609 |
| Other Net Income | 16,500 |
| Other Revenues | 513,562 |
| Revenue from Contract with Customer | 0 |
| Selling and General Administrative Expense | 339,531 |
Output Variables
The output variables are the absolute values as calculated by the valuation model.
| Output Variables | in 1000 USD |
|---|---|
| Liabilities | 1,381,795 |
| Assets | 2,017,100 |
| Expenses | 770,194 |
| Revenues | 513,562 |
| Stockholders Equity | 635,305 |
| Net Income | -240,132 |
| Comprehensive Net Income | -240,132 |
| Economic Capital Ratio | 23% |
Feature Distribution
The Feature Distribution illustrates the distribution of the model variables' effect values across the industry. The specific effect of the company in question within this distribution is indicated by a black arrow. The top two charts highlight the company's greatest strengths, whereas the bottom two charts reveal its most significant weaknesses.
Strengths and Weaknesses Over Time
The strengths and weaknesses plot shows how the company's greatest strengths and weaknesses develop over time. The corresponding impact measures the percentage point increase or decrease in the Economic Capital Ratio.
Keyfigures Over Time
The Key Figures over Time display tracks the development of assets and liabilities from the balance sheet, along with revenues and expenses from the profit and loss statement, over time.
Regression
The Regression compares the forecasted company valuation with the observed stock market values. A positive correlation suggests that the model effectively explains market prices. A company's valuation above the regression line indicates that the company is overvalued, otherwise it is undervalued.

Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet plot illustrates the evolution of Assets and Liabilities over time. The difference between them, known as Equity, represents the accumulation of past profits.

Profit & Loss
The Profit & Loss plot shows the development of Revenues and Expenses over time. The difference between these, either as Profit or Loss, reflects the surplus from the previous year.

Industry Index
The RealRate Index shows how financial health develops over time. The blue line shows the evolution of the Economic Capital Ratio for the individual company. This is compared to the distribution of all other companies. The change in the company's financial strength is shown in the lower part.